Procut Class
Greenhouse -- the main force of future agricultural development
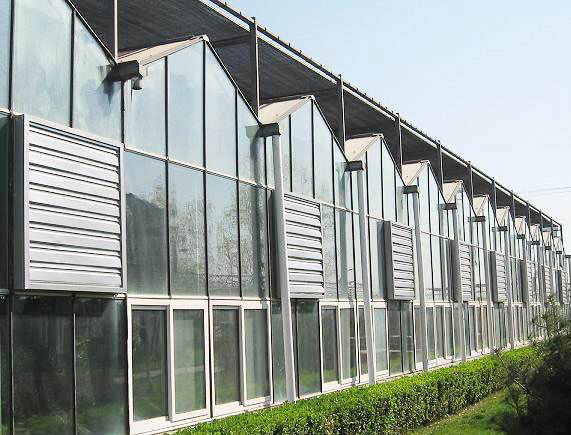

Shandong Muchen Agricultural Development Co., Ltd. is a professional greenhouse manufacturer specializing in the design and processing of all kinds of greenhouses and supporting facilities. It produces flower market greenhouses, planting greenhouses, aquatic products, animal husbandry greenhouses, glass greenhouses, sunlight plate greenhouses, film multi span greenhouses, sunlight greenhouses, ecological restaurant greenhouses and greenhouse accessories and supporting equipment. Our company can process and manufacture the greenhouse skeleton with the width of 8 meters, 9.6 meters, 10.8 meters and 12 meters, as well as the special skeleton for the ecological restaurant with high ridge, large span and large bay. The building width is 9.6-12 meters, the column height is 6-8 meters and the bay is 6-8 meters. The appearance is beautiful, the internal vision is broad, spacious and bright.
In the use of greenhouse, there are still problems of low utilization rate and low economic benefit. At present, in the use of plastic greenhouse, we should pay attention to the rational arrangement of stubble, so as to make the greenhouse give full play to its role and achieve the purpose of increasing income. Stubble arrangement can be divided into three basic types:
1) Stubble type dominated by cultivation. The greenhouse consists of three crops: Dry Cultivation in spring (pepper, tomato, cucumber, green beans, etc.), delayed cultivation in autumn (pepper, tomato, etc.) and seedling raising in winter (eggplant, melon, beans). Spring starts in late February. After the planting of eggplant, fruit and melon seedlings, small arch shed shall be covered with straw fence for thermal insulation, and they can be put on the market in mid and late April. Delayed cultivation of tomatoes and peppers in autumn, good antifreeze and heat preservation in the later stage, which can be put on the market until new year's day. In winter, tomato, pepper and eggplant seedlings (3-4 real leaves) are mainly cultivated by multi-layer mulching in the shed, and the last crop of vegetables should be finished in mid November. The above arrangement focuses on early maturing in spring. Pay attention to sufficient fertilizer and high level of cultivation technology in order to achieve the expected purpose.
2) Stubble type dominated by seedling raising. It is composed of seedling raising in winter, seed retention in spring and delayed cultivation of blue stubble in autumn. The seedling raising starts from December, and an electric hotbed is set in the shed, which can be sown directly. The seedlings that can also be raised in the hotbed are planted in the cabinet, and small arch flail and grass fence should be used to keep warm during overwintering. After the seedlings are raised in spring, the parents for pepper or tomato seed production (or the original seeds of various parents) are planted in the shed for hybrid seed production. As long as we master the seed production technology, such as the first generation hybrid Zaofeng 1 of pepper, the yield per mu can reach 2000-2500 kg. Autumn stubble is still carried out as usual, with tomato and pepper as the majority. This stubble arrangement has high economic benefits and can cultivate strong seedlings for a large area of vegetable field.
3) Stubble type mainly for seed production and retention. It consists of three stubbles: seed retention in winter and spring, seedling raising in summer and delayed cultivation in autumn. In winter and spring, it is used for seed preparation and seed retention of Brassica campestris, cabbage and other sparse vegetables of Cruciferae. Generally, seed plants are planted in December, and the canopy film is kept for rain protection after spring reflection. Plastic yarn apron is used around the skirt film to prevent insect pollination and ensure seed quality. Autumn tomato, cauliflower and other vegetable seedlings can be cultivated in this shed in the middle and late July. In addition, it can also be used for the preparation of first-generation hybrids in spring and delayed cultivation in autumn. This arrangement is mostly used in improved seed breeding farms and agricultural scientific research institutions.

 中文版
中文版 English
English Soilless cultivation
Soilless cultivation Multi span greenhouse
Multi span greenhouse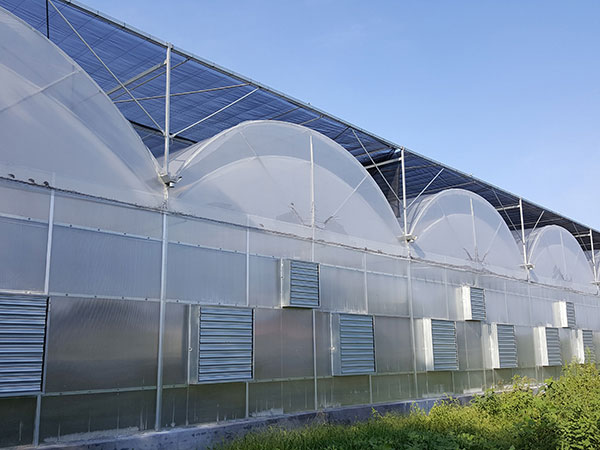 Polycarbonate greenhouse
Polycarbonate greenhouse Ecological Restaurant
Ecological Restaurant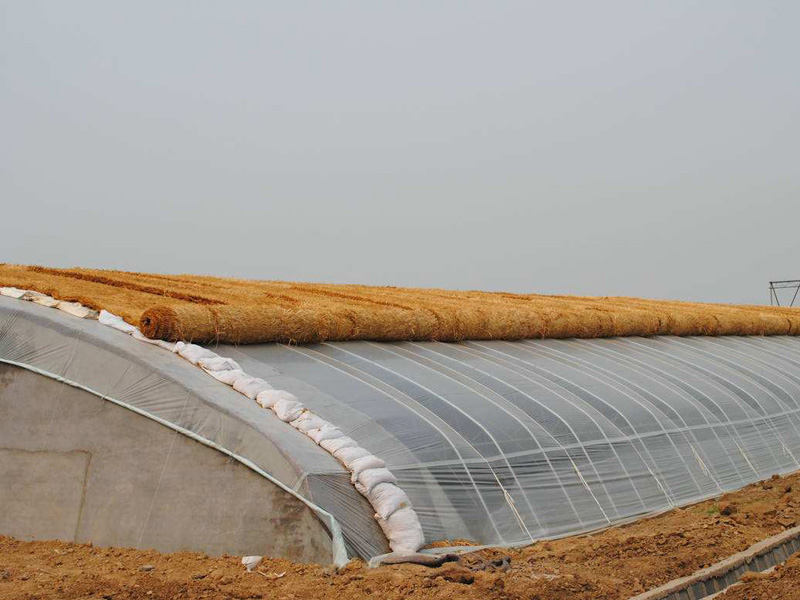 Solar greenhouse
Solar greenhouse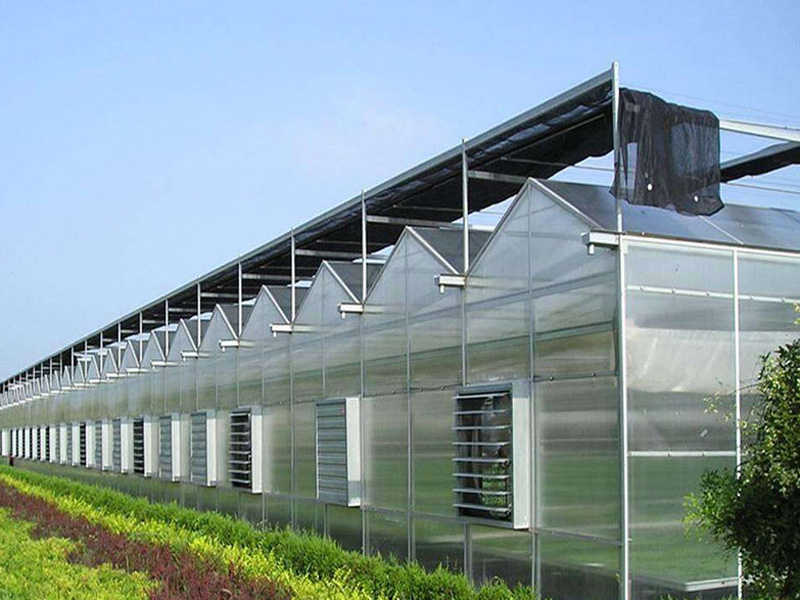 Venlo greenhouse
Venlo greenhouse Intelligent glass greenhouse
Intelligent glass greenhouse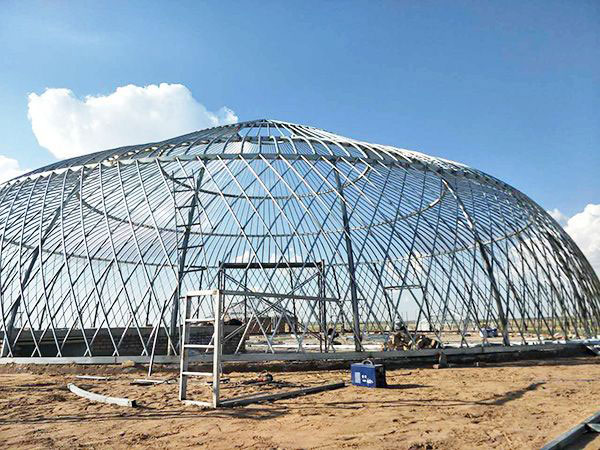 Bird's nest type spherical greenhouse
Bird's nest type spherical greenhouse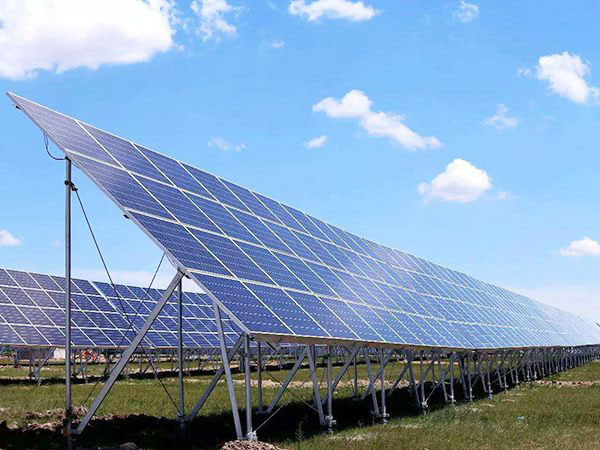 Photovoltaic greenhouse
Photovoltaic greenhouse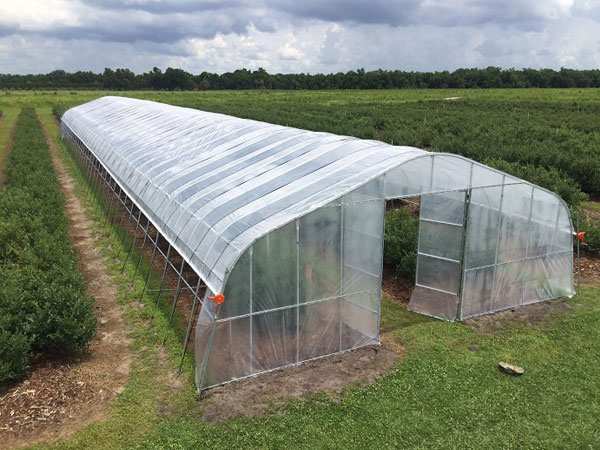 Tunnel greenhouse
Tunnel greenhouse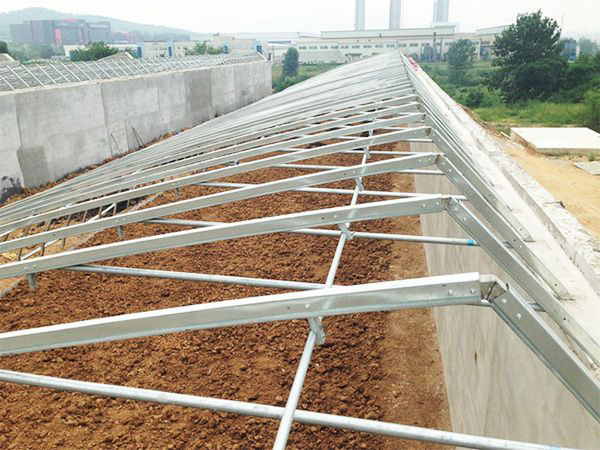 Steel structure greenhouse
Steel structure greenhouse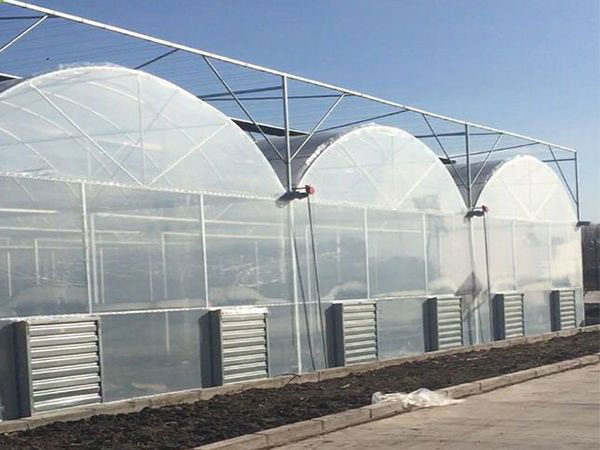 Film greenhouse
Film greenhouse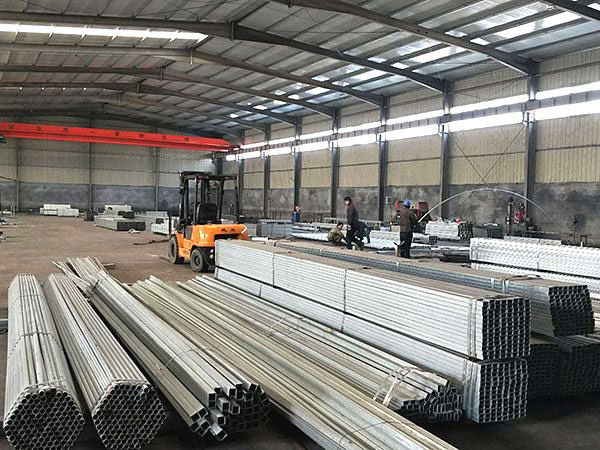 Greenhouse accessories
Greenhouse accessories Soilless cultivation
Soilless cultivation Scan, wechat consulting
Scan, wechat consulting
